
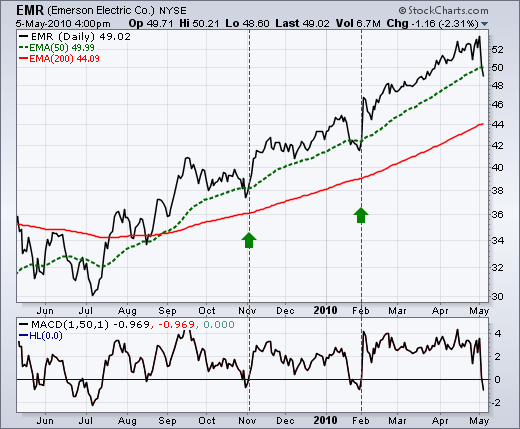
In an uptrend, take a long position when the 12 period EMA is above the 26 period EMA during an intraday basis.Īnother popular EMA Strategy used by Forex traders is the crossover of short and long term time periods such as the 20 and 50 day EMAs for trading signals. Note the market slope on both the 12 and 26 day periods. Once the trade has been placed and closes below 26-day EMA, the moving average is now out of date.Ĭ. Place a Stop Loss one pip pips below 26 EMA nearest the swing point levelĪ.ěase on a 1:2 setup or once stop losses have been triggeredī. Protect your Investment against False BreakoutsĪ.Bullish momentum now strongly implicates a bullish market. This allows the market to develop and prove the trendĪ.Ět the third successful EMA Crossover, buy at market price. Wait for two successful EMA Crossovers between 12 and 26 day EMAsĪ.A simple EMA Crossover above to 26-day EMA may not be bullish enough to warrant a higher price push if bought for profit.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_Final_Exponential_Moving_Average_EMA_Aug_2020-01-3bacd080c9ac450595fe7daa9148a65b.jpg)
Markets are easily susceptible to false breakouts.
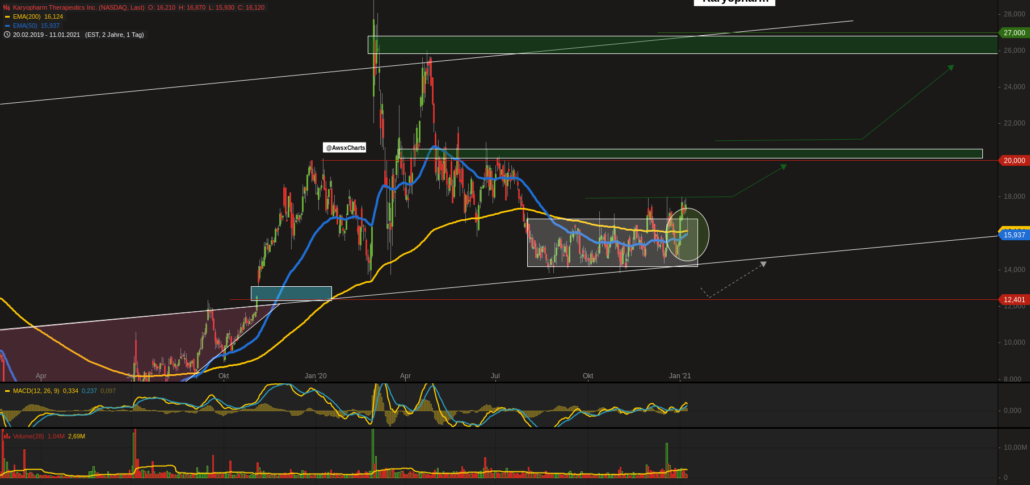
This strategy is a combination of two specific EMAs, one with a period of 12 days and another with 26 days. An example has been provided below for a buy trade in a bullish market. It is widely popular amongst Forex trading. One commonly used EMA Crossover Strategy is the EMA 12 and EMA 26. The goal of the EMA Crossover Strategy is to capture a new trend by utilizing two EMAs, one with a long period and one with a short period. The use of an EMA Crossover Strategy can help identify market upward or downward trends and provide support or resistance to trading within them.įorex traders tend to utilize a short-term moving average crossover long-term moving average over various timed intervals, currency pairings and band percentages. Trades placed should then not deviate from that direction. Trades based on EMA should be executed once a strong trend has been indicated. Trading below the moving average results in lower prices.
#20 ema 200 ema how to
How to identify when to use an Uptrend EMA Strategy vs a Downtrend EMA Strategy Multiplier = (2 / (Time periods + 1) ) = (2 / (20 + 1) ) = 0.0952(9.52%)ĮMA = x multiplier + EMA(previous day).ĮMAs will react faster to price changes than the SMA due to the weight placed on the recent pricing data available. Example Formula: 20-day EMAĢ0-day EMAs follow prices closely and produce minimal lag in price reversals when compared with 50 or 100-day longer-term EMAs. Then, we add the EMA of the previous day. We do this by subtracting the closing price from the previous period’s EMA and multiply it by our time period multiplier. Once the SMA price and time period multiplier have been determined, we must calculate the EMA.
#20 ema 200 ema software
Most trading platforms come equipped with charting software that does these calculations for the trader, but a breakdown of the formula is provided formula below.
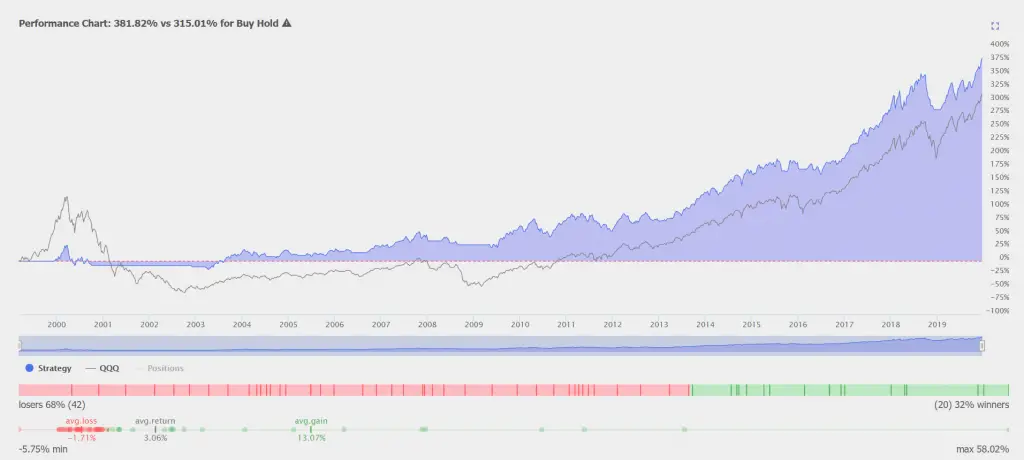
Some commonly used time periods for EMA analysis are 10, 20, 50, and 100 days, but most traders use time periods between 10 and 100 days with bands of 1-10% distance between moving averages. We can calculate the SMA by summing the number of time periods included and divide by a multiplier that focuses the moving average indicator’s curve.Īny time period can be utilized: 10 days, 30 minutes, 40 weeks, etc. The Simple Moving Average (SMA) is used as the starting point of the range of prices used to calculate the EMA value. The EMA Strategy does not predict the market but instead aids in the analysis of current market conditions, thus making it a more reliable source of either support or resistance for trading strategies by placing emphasis on the most recent prices. The Exponential Moving Average, also referenced as an EMA Trading Strategy, is a widely utilized and one of the most well-established methods of technical analysis for identifying market trends across any and all markets.īy using a mathematical formula, the Exponential Moving Average calculates the constant average price reflected over a specified period of time or “lookback period.” Shorter look back periods will result in more volatile reactions due to the involvement of price changes. How to Trade With The Exponential Moving Average Strategy How to identify when to use an Uptrend EMA Strategy vs a Downtrend EMA Strategy.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
